Anime Robots Evolved Hand-in-Hand with Toys
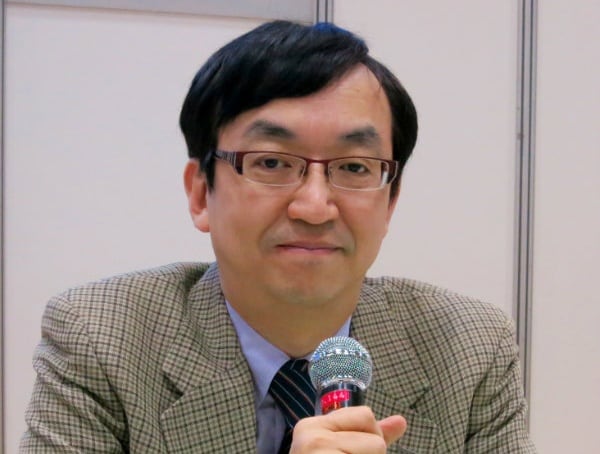
“Transformers, the action film series featuring humanoid robots, have become global hits, but they trace their roots to the Japanese genre of robot anime,” says Ryusuke Hikawa, an anime and live action film critic who is also a visiting professor at Meiji University’s Graduate School of Global Japanese Studies.

http://www.gov-online.go.jp/eng/publicity/book/hlj/html/201602/201602_08_en.html
A researcher of Japanese animation technology and culture, Hikawa delves into this subgenre and what he says is its central role in Japanese culture and a reflection of Japanese sensibilities.
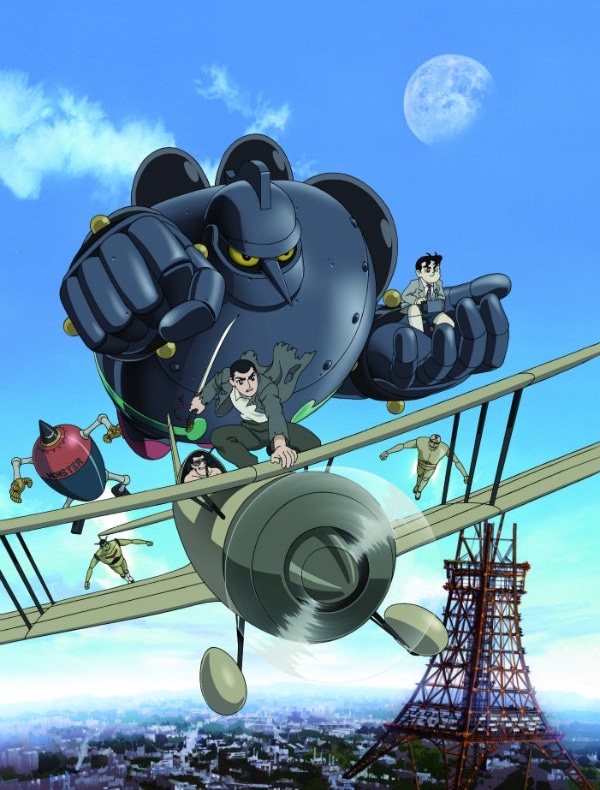
Robot anime emerged in Japan over half a century ago in 1963, when Osamu Tezuka’s Tetsuwan Atomu (Astro Boy) appeared as the first anime program on television. Mitsuteru Yokoyama’s Tetsujin 28-go debuted the same year. These two shows marked the beginning of Japanese TV animation, which now boasts over two hundred titles broadcast each year.

http://www.gov-online.go.jp/eng/publicity/book/hlj/html/201602/201602_08_en.html
While Astro Boy is a life-sized autonomous robot with free will like humans, Tetsujin is a massive remote-controlled automaton. Interestingly enough, these two styles typify the two main kinds of robots found in Japanese industry today.
Robot anime took off following the late 1972 broadcast of Mazinger Z, based on a graphic novel created by Go Nagai with the intention of making it into an animated TV show. In this series, a vehicle merges with the robot’s head, and a human rider directly controls the robot, resulting in a new style of human-powered “mecha.” This can also be considered an advanced version of the “transformation” seen in live-action programs like Ultraman and Kamen Rider, and it entranced children.
Partway through Mazinger Z’s run, zinc alloy toys of the character went on sale under the “Super-Alloy” brand, riffing on elements from the show. The toys were a smash hit. These metallic figures had a cold feel and notable heft, as well as a spring-loaded contraption and mechanical switches that controlled the signature “rocket punch” maneuver used to take down villains in the TV show. Refined industrial technology succeeded in making the fantasy of the anime world a reality.
http://www.gov-online.go.jp/eng/publicity/book/hlj/html/201602/201602_08_en.html
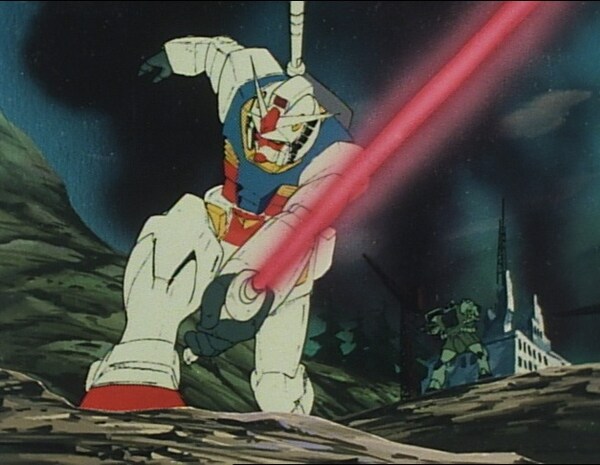
In 1979, a new, epoch-making program was born: Mobile Suit Gundam. Developed by director Yoshiyuki Tomino and his team, the Gundam series had a unique worldview. Its story targeted audiences of middle and high schoolers or older, and for that reason toy merchandise sales struggled during its initial run. However, the 1980 release of the build-it-yourself Gundam plastic model, or gunpla for short, proved to be its turning point, and sales continue to hold strong to this day.
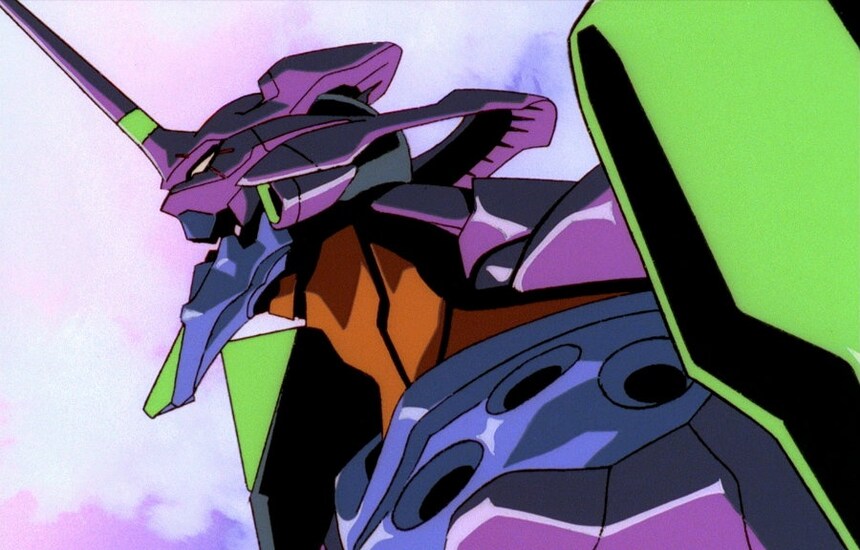
The success of the Gundam series led to the production of countless original animation series, which in turn inspired a new generation. In 1995, a new robot anime aimed to succeed based on the merits of its story alone, becoming a social phenomenon: Hideaki Anno’s Neon Genesis Evangelion. The show emulated Mazinger Z with a narrative structure in which humankind’s science and technology were used to intercept mysterious monsters, yet it adopted biotechnologies and hybrid components that allowed an external suit of armor to be connected to the internal operator’s nerves and spiritual energy.
Read full story: www.gov-online.go.jp
NEON GENESIS EVANGELION / Director Hideaki Anno © KharaProject Eva
Tetsujin 28-go © HIKARI PRODUCTION / SHIKISHIMA JYUKOU
Mobile Suit Gundam © SOTSU-SUNRISE




